Successful Initial Launch I Digital Twin Supports CHAM to Increase Capacity
-
Company News
-
2024-05-31
A New Force, the Booming Battery Market
The rise of electric vehicles and renewable energy has caused the battery business to surge in recent years, with worldwide electric vehicle sales predicted to grow at a 25% annual rate until 2030. The market demand for high-performance battery technology is increasing as consumers desire longer battery life, faster charging, greater safety, and lower costs.
The year 2023 is regarded as the first year of widespread application of a number of new technologies, the promotion of which has increased battery safety and economy while hastening the development of new energy vehicles and energy storage. The global battery industry is experiencing a yearly increase of approximately 14% in patent applications, showcasing the industry’s innovation efforts and the strong research and development capabilities of companies.
Challenges and Opportunities
Dealing with fluctuating raw material expenses, rising competition, and the unpredictability of technological advancements are all obstacles that must be tackled. However, these difficulties also offer chances for diversifying supply chains, innovating technologically, and optimizing models.
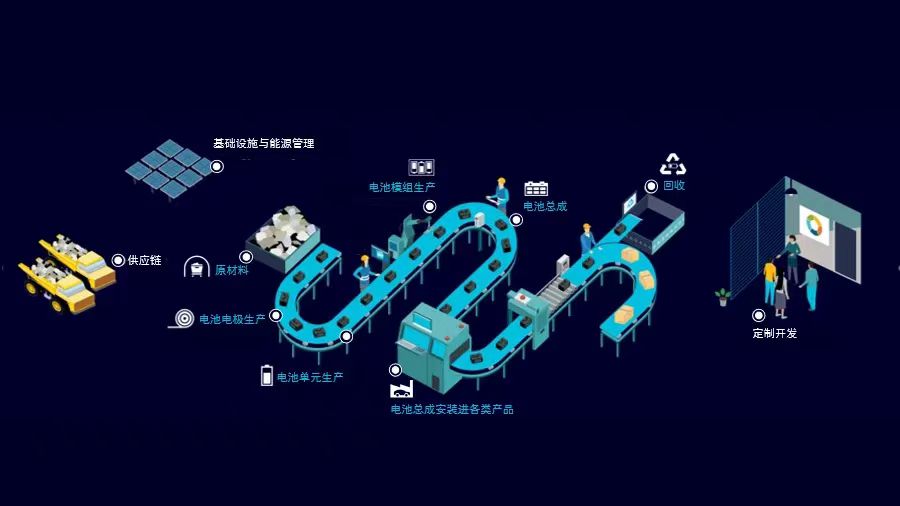
This diagram illustrates the battery production life cycle, showing that various digital technologies are utilized throughout the entire process, including sourcing raw materials, manufacturing, and battery recycling. When expanding the primary manufacturing steps, there are typically 9 key processes involved in producing cells from raw materials into poles. The whole manufacture takes 3-5 weeks or potentially longer. It encompasses various typical process manufacturing characteristics such as pulp, coating, batch processing, assembly, material selection, and other discrete manufacturing features. The complexity of battery manufacturing process poses significant challenges when it comes to planning a battery plant.
Hence, during the establishment of CHAM Mianyang’s new battery plant, CHAM is actively looking for help from Digital Twin and other advanced methods to guarantee the precision of the design plan, enhance production efficiency, and elevate product quality.
CHAM Mianyang Utilizes Digital Twin to Support plant Planning
Shenzhen CHAM New Energy Co., Ltd. (referred to as “CHAM”) is one of the initial private companies in China to produce cylindrical lithium-ion batteries on a large scale. With over 20 years of experience in the industry, CHAM has emerged as a prominent provider of diverse new energy solutions in China. The company boasts a skilled R&D team and offers full product solutions.
The CHAM Mianyang Cylindrical Lithium Battery Production Base is a local digital plant supported by Siemens, featuring completely automated production lines developed domestically, promoting a significant level of automation and intelligence, and setting a new benchmark for the progress of China’s manufacturing industry. The products are mainly used in low-power, medium-power, and energy storage applications, including electric vehicles, electric motorcycles, home energy storage systems, energy storage for base stations, and energy storage for industrial and commercial purposes. Once full production is finished, the annual output value is expected to surpass 20 billion yuan, establishing the plant as a leading company in the large cylindrical battery industry.
Utilizing Simulation & Digital Twin can facilitate the transition from plant planning to operation, improve decision-making by conducting iterative experiments and optimizations, mitigate risks, cut costs, expedite decision-making, and assist CHAM in achieving “successful initial launch” in battery plant planning.

8% capacity increase, significantly reducing hardware equipment investment and production costs
CHAM and Siemens China Research Institute collaborated to address various pre-operational design challenges using Simulation & Digital Twin technology as they navigated towards establishing a native digital plant. For instance, when it comes to creating automated drying cells post battery assembly, the intricate nature of the process poses challenges in accurately forecasting the potential production output. This is mainly due to the various optional equipment sets and shared manipulators involved, leading to uncertainties regarding the reliability of the solution and its ability to meet industry standards. By utilizing Digital Twin, the two companies collaboratively identified crucial bottlenecks in the production process and successfully streamlined them, resulting in an 8% boost in capacity without extra equipment investment. Furthermore, thorough simulation tests were conducted to guarantee that the distribution of resources was maximized considering capacity and material availability. Specifically, half of the investment in the stacking machine and four AGVs were reserved solely for the quick chemical compartmentalization process. By implementing a series of optimization strategies, not only is the expenditure on hardware equipment minimized, but the overall production expenses are also substantially decreased.
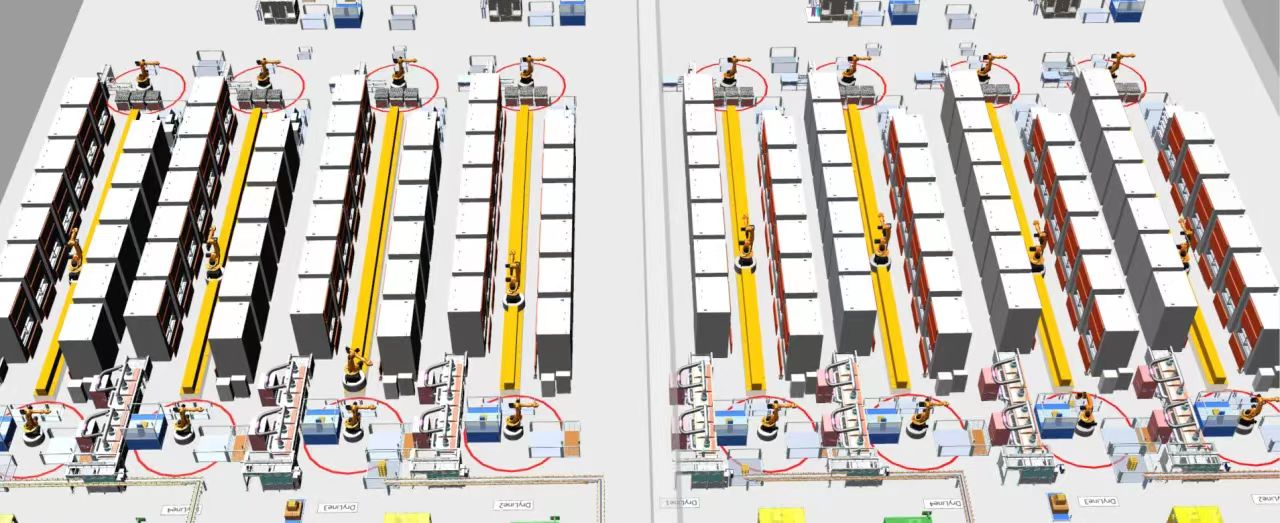
The hypothetical analysis further identifies and avoids five major potential risks that may be encountered in future operations, including insufficient capacity of ambient storage, congestion on roller conveyors, and a shortage of buffer areas. This process not only improves production efficiency, but also facilitates the development of targeted response strategies to ensure the stable operation of the battery plant.
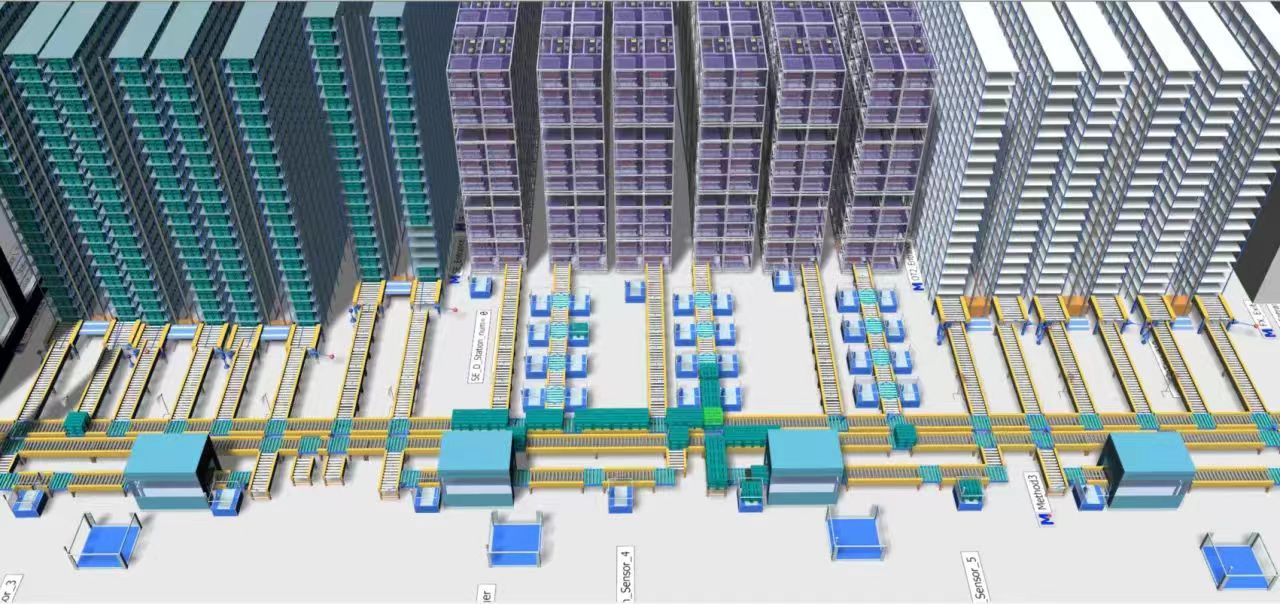
While working on the project, CHAM participated in the DT LAB Co-Creation Workshop where they collaborated with experts from Siemens China Research Institute to address and create effective solutions for important issues. This collaboration aimed to advance technology and innovation, setting a strong groundwork for future sustainable development.

Simulation & Digital Twin, a major focus in Siemens’ core technology field, aims to assist businesses in achieving more environmentally friendly, secure, and productive product and production cycles. In the present day, this technology has evolved into a potent tool and core principle for digital advancement. It involves combining models and data throughout the value chain to assist various teams such as plant operations managers, production line engineers, product designers, after-sales service teams, and building operations management teams. The Digital Twin not only efficiently plans and monitors systems in real-time, forecasts trends, and offers valuable insights, but also allows for closed-loop optimization of systems, reduces design cycles, and enhances economic efficiency and quality.
The CHAM Mianyang plant is the 10th digital twin plant planning project that I have participated in. My team and I were primarily in charge of the planning of the digital twin plant. This included the DT LAB co-creation workshop conducted by Huiling and Haili, as well as the simulation modeling and analysis led by Zhou Wei and Liu Zhao. I was amazed by the numerous creative features integrated into the new plant, showcasing the strong determination and forward-thinking of CHAM’s leadership, which also positively impacted the project team.
---- Project Manager Xiang Zhimou






